1. Introduction
This primer is intended to accompany [SAI]. It is focused on providing a friendly introduction for developers of libraries intended for solid authorization agents.
This document was developed alongside the open-source TypeScript implementation [SAI-JS] and open-source Java implementation [SAI-JAVA].
2. Shape Tree
Shape Trees [SHAPETREES] allow for the definition and validation of data hierarchies including which shapes [SHEX] should be used to validate data. In our examples, we are going to use the following Shapes and Shape Trees.
solidtrees : Project a shapetrees : ShapeTree ; shapetrees : expectsType shapetrees : Resource ; shapetrees : shape solidshapes : Project ; shapetrees : references uuid : 54b5e4f6-c6b5-4c9a-b885-cbf69d08370d . uuid : 54b5e4f6-c6b5-4c9a-b885-cbf69d08370d shapetrees : hasShapeTree solidtrees : Task ; shapetrees : viaShapePath "@<https://solidshapes.example/shapes/Project>~<https://vocab.example/project-management/hasTask>" .
solidshapes : Project { a [ pm : Project ] ; rdfs : label xsd : string ; pm : hasTask IRI * }
solidtrees : Task a shapetrees : ShapeTree ; shapetrees : expectsType shapetrees : Resource ; shapetrees : shape solidshapes : Task .
solidshapes : Task { a [ pm : Task ] ; rdfs : label xsd : string }
Reference shape path documentation
3. Registry Set
Authorization Agent uses a set of different registries to perform its dutes. Specificaly,
-
one or more § 4 Data Registry,
-
one § 6 Agent Registry,
each one of them is described in a dedicated section.
The Registry Set can be discovered from a social agent’s WebID Profile using interop:hasRegistrySet predicate.
alice : \#id a interop : Agent ; interop : hasRegistrySet alice-auth : 13e60d32-77a6-4239-864d-cfe2c90807c8 ; interop : hasAuthorizationAgent <https://auth.alice.example/> .
While WebID Profile is readable to the public, Registry Set should only be readable by its owner and their Authorization Agent.
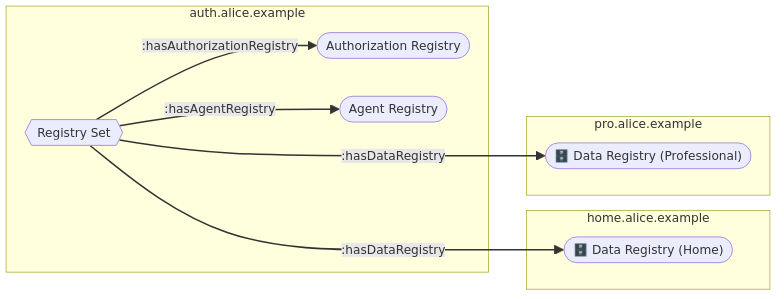
alice-auth : 13e60d32-77a6-4239-864d-cfe2c90807c8 a interop : RegistrySet ; interop : hasAgentRegistry alice-auth : 1cf3e08b-ffe2-465a-ac5b-94ce165cb8f0 ; interop : hasAccessConsentRegistry alice-auth : 96feb105-063e-4996-ab74-5e504c6ceae5 ; interop : hasDataRegistry alice-pro : 71e96aaa-f3dc-4263-97d6-a5b4c83524cb , alice-home : 2d3d97b4-a26d-434e-afa2-e3bc8e8e2b56 .
4. Data Registry
A Data Registry is a collection of Data Registrations, each of which represents a unique type of data, identified by a shape tree.
alice-pro : 71e96aaa-f3dc-4263-97d6-a5b4c83524cb a interop : DataRegistry ; interop : hasRegistration alice-pro : 773605f0-b5bf-4d46-878d-5c167eac8b5d , alice-pro : 4d594c61-7cff-484a-a1d2-1f353ee4e1e7 .
In a Data Registry, there can be at most one Data Registration for any given shape tree.
4.1. Data Registration
Data Registration is a container, which contains Data Instances. Each of those Data Instances conforms to one specific shape tree assigned to the Data Registration.
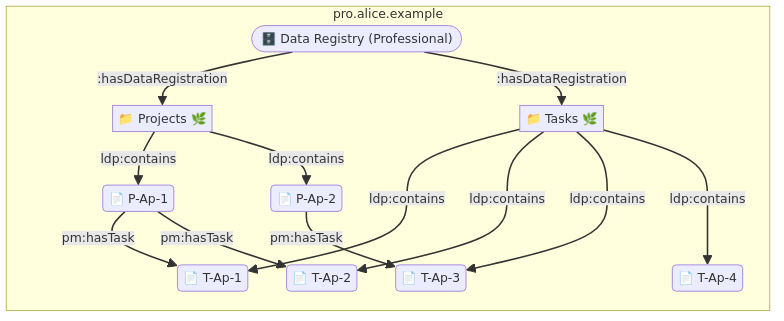
alice-pro : 773605f0-b5bf-4d46-878d-5c167eac8b5d a interop : DataRegistration ; interop : registeredShapeTree solidtrees : Project ; interop : registeredAt "2020-10-17T11:42:35.000Z" ^^ xsd : dateTime ; interop : registeredBy <https://alice.example/#id> ; interop : registeredWith <https://solidmin.example/#app> ; interop : iriPrefix "https://pro.alice.example/" ; ldp : contains alice-pro : ccbd77ae-f769-4e07-b41f-5136501e13e7\#project , alice-pro : 7a130c38-668a-4775-821a-08b38f2306fb\#project .
- registeredShapeTree
-
Shape Tree used by this Data Registration
4.2. Data Instance
Data Instance is a resource representing something specific, for example, a project or a task. An Authorization Agent is not responsible for modifying data instances. Sometimes it still needs to access them during § 7 Gathering Authorizations from the user if the user wants to select specific data instances.
5. Authorization Registry
Authorization Registry is a container, which contains Access Authorizations. Each of those Access Authorizations is created for a specific grantee, and groups together one or more Data Authorizations.
alice-auth : 96feb105-063e-4996-ab74-5e504c6ceae5 a interop : AccessConsentRegistry ; interop : hasAccessConsent alice-auth : eac2c39c-c8b3-4880-8b9f-a3e12f7f6372 , alice-auth : 75a2ef88-d4d4-4f05-af1e-c2a63af08cab .
5.1. Access Authorization
Access Authorization groups one or more data authorizations. Together they represent the whole access granted by a social agent to another agent. One of the primary responsibilities of the authorization agent is § 9 Generating Access Grant from Access Authorization.
An Access Authorization is immutable, it never gets updated, instead it can be only replaced with a newer Access Authorization.
5.2. Data Authorization
Data Authorization, similar to § 6.7 Data Grant, represents access granted by a specific Social Agent.
It is always associated with a specific § 2 Shape Tree. Depending on its scope it can apply to all the
Data Instances in any number of Data Registrations. In that case, interop:hasDataRegistration will not be specified.
alice-auth : e2765d6c-848a-4fc0-9092-556903730263 a interop : DataConsent ; interop : grantedBy <https://alice.example/#id> ; interop : grantedWith <https://jarvis.alice.example/#agent> ; interop : grantee <https://projectron.example/#app> ; interop : registeredShapeTree solidtrees : Project ; interop : dataOwner <https://acme.example/#corp> ; interop : accessMode acl : Read , acl : Write ; interop : scopeOfConsent interop : AllFromAgent . alice-auth : 6a9feb57-252b-43b2-8470-5a938888b2fa interop : inheritsFromConsent alice-auth : e2765d6c-848a-4fc0-9092-556903730263 .
A Data Authorization is immutable, it never gets updated, instead it can be only replaced with a newer Data Authorization.
5.2.1. Scopes
Data Authorization can have one of five scopes:
- All
-
All the Data Instances in all the Data Registration the End-user has access to. This includes ones owned by the End-user as well as ones owned by others, where End-user has been granted access.
- AllFromAgent
-
All the Data Instances in all the Data Registrations, owned by a specific social agent. This could be the End-user themselves or any other social agent who granted access to the End-user.
Plus all the Data Grant Scopes
6. Agent Registry
alice-auth : 1cf3e08b-ffe2-465a-ac5b-94ce165cb8f0 a interop : AgentRegistry ; interop : hasSocialAgentRegistration alice-auth : b1f69979-dd47-4709-b2ed-a7119f29b135 , alice-auth : 5dc3c14e-7830-475f-b8e3-4748d6c0bccb ; interop : hasApplicationRegistration alice-auth : bcf22534-0187-4ae4-b88f-fe0f9fa96659 , alice-auth : 170c12ac-7d4f-47fe-b36d-7a9944c429d9 .
6.1. Agent Registration
There can be only one Agent Registration for any given agent in Agent Registry. Its main purpose is to make § 6.6 Access Grant available to the registered agent.
6.2. Social Agent Registration
Social Agent Registration is created for a Social Agent. Besides § 6.6 Access Grant it can also reference a § 6.2.1 Reciprocal Registration.
6.2.1. Reciprocal Registration
The reference to reciprocal registration can be created after receiving an § 6.8 Access Receipt from another Social Agent and performing § 6.5 Agent Registration Discovery
In the case of Social Agent Registration for ACME, created in Alice’s Agent Registry. The reciprocal registration will be the Social Agent Reigstration for Alice, created in ACME’s Agent Registry.
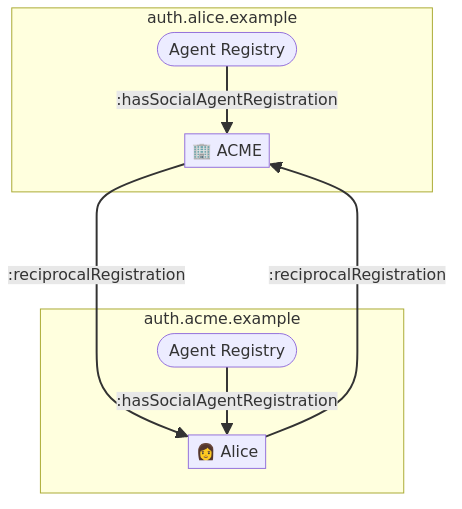
6.3. Social Agent Invitation
Social Agent Invitation represents an invitation for a Social Agent. It takes advantage of an existing and secure
communication channel between two agents to pass a secret link that allows accepting the invitation.
This flow results in both agents establishing a pair of Reciprocal Registrations.
If the platform supports it, the Authorization Agent of the sender can use [WEB-SHARE] to pass the secret
link to the user’s messaging app. On the other side, the Authorization Agent of the recipient can use
[WEB-SHARE-TARGET] to register with the platform and receive a secret link from the user’s messaging app.
Independent of the platform, Authorization Agents should always allow a simple copy of the link by the sender
(e.g., navigator.clipboard.writeText) and paste it by the recipient.
6.4. Application Registration
Application Registrations are created by the End-user for applications they use. Since applications do not own or share data, they will never have a [#reciprocal-registration].
6.5. Agent Registration Discovery
Both Social Agent and Application can discover Agent Registration created for them,
by performing HEAD or GET request on IRI denoting
the Authorization Agent. Response will include HTTP Link header relating
Agent Registration to the agent making the request using
http://www.w3.org/ns/solid/interop#registeredAgent
as link relation.
In a case where End-user using an application performs the discovery on their own Authorization Agent. The response will include a link to the Application registration.
HEAD / HTTP / 1.1 Host : auth.alice.example Authorization : DPoP ....
HTTP / 1.1 200 OK Link : <https://projectron.example/#app>; anchor="https://auth.alice.example/bcf22534-0187-4ae4-b88f-fe0f9fa96659"; rel="http://www.w3.org/ns/solid/interop#registeredAgent"
In the case where the client acting on behalf of one social agent, performs the discovery on another’s social agent Authorization Agent. The response will include a link to Social Agent Registration.
HEAD / HTTP / 1.1 Host : auth.alice.example Authorization : DPoP ....
HTTP / 1.1 200 OK Link : <https://bob.example/#id>; anchor="https://auth.alice.example/92868ad4-a9e6-42df-9cb0-883350c62769"; rel="http://www.w3.org/ns/solid/interop#registeredAgent"
6.6. Access Grant
An Access Grant groups together all the Data Grants provided for a specific agent.
An Access Grant is immutable — it never gets updated; it can only be replaced, by a newer Access Grant.
6.7. Data Grant
Each Data grant represents access granted by specific Social Agent, to all or selected Data Instances in specific Data Registration.
alice-auth : cd247a67-0879-4301-abd0-828f63abb252 a interop : DataGrant ; interop : dataOwner <https://alice.example/#id> ; interop : grantedBy <https://alice.example/#id> ; interop : registeredShapeTree solidtrees : Project ; interop : hasDataRegistration alice-pro : 773605f0-b5bf-4d46-878d-5c167eac8b5d ; interop : accessMode acl : Read , acl : Write ; interop : scopeOfGrant interop : SelectedFromRegistry ; interop : hasDataInstance alice-pro : 7a130c38-668a-4775-821a-08b38f2306fb\#project . alice-auth : 9827ae00-2778-4655-9f22-08bb9daaee26 interop : inheritsFromGrant alice-auth : cd247a67-0879-4301-abd0-828f63abb252 . alice-pro : 773605f0-b5bf-4d46-878d-5c167eac8b5d interop : iriPrefix "https://pro.alice.example/" .
A Data Grant is immutable, it never gets updated, instead it can be only replaced with a newer Data Grant.
Data Grant can be consider as the most important data structure, it provides following information:
- dataOwner
-
Social Agent who owns the data
- grantedBy
-
Social Agent who granted the access
- registeredShapeTree
-
Shape Tree used by related Data Registration
- hasDataRegistration
-
Data Registration that this Data Grant applies to. As well as
iriPrefixof that Data Registration (see § 4.1 Data Registration) - accessMode
-
List of access modes defining what application can do with the data
- scopeOfGrant
-
Defines which instances can be accessed (see § 6.7.1 Scopes)
- inheritsFromGrant
-
If grant has
InheritInstancesscope, it will be the Data Grant for Data Registraion with parent Data Instances (see § 6.7.2 Inheritance) - hasDataInstance
-
If grant has
SelectedInstancesscope, it will be all the Data Instances that application can access in the Data Registration - delegationOfGrant
-
If Data Grant is issued by Social Agent other than data owner, it will be the original Data Grant issued by the data owner (see § 6.7.3 Delegation)
6.7.1. Scopes
Data Grant can have one of three scopes:
- AllFromRegistry
-
All the Data Instances in the Data Registration. Application will be able to access the Data Registration and see the list of all contained instances (see § 4.1 Data Registration)
- SelectedFromRegistry
-
Only specific Data Instances in the Data Registration. Application will not be able to access the Data Registration, so it will not see the list al all contained instances. Instad list of selected Data Instances is available via
hasDataInstance - Inherited
-
Only those Data Instances in the Data Registration, which are related to parent kData Instances in Data Registration of the Data Grant referenced with
inheritsFromGrant(see § 6.7.2 Inheritance)
6.7.2. Inheritance
InheritInstances Data Grant doesn’t provide access to the Data Registration, so
application can’t get the list of all the Data Instances. Neither it provides a list of specific
Data Instances in the Data Registration.
To find Data Instances from that Data Registration, application first needs to access parent
Data Instances from Data Registration which Data Grant referenced by inheritsFromGrant
makes accessible. Based on shape tree definition, each parent Data Instance will reference all its
child Data Instances.
Both parent and child Data Registrations have to be in the same Data Registry. Since only one Data Registration for specific shape tree can be created in any given Data Registry. All parent Data Instances are from one Data Registration and all child Data Instances are from one Data Registration.
6.7.3. Delegation
Application doesn’t need to handle delegated Data Grants in any special way.
To know if Data Grant was issued by currently logged in user or someone else,
application should rely on dataOwner information in the Data Grant.
6.8. Access Receipt
Access Receipt helps to establish data sharing between two social agents. Once received the authorization agent should prompt the user to approve creating § 6.2 Social Agent Registration for that data owner. If user approves § 6.2.1 Reciprocal Registration can be associated and subscription for notifications established to keep track on the latest § 6.6 Access Grant. Once reciprocal registration gets associated there is no further need for its data owner to send access receipts to the agent registered in that reciprocal registration.
6.9. Access Need Group
An Access Need Group is a collection of Access Needs used to communicate an access request to Social Agents.
An Authorization Agent uses them during § 7 Gathering Authorizations from the user.
6.10. Access Need
An Access Need represents the requirement of one specific type of data represented by a shape tree, as part of an Access Need Group.
Complete this section based on implementation of UI for Authorization Agent Service
7. Gathering Authorizations from the user
The most common case is authorizing an application based on its § 6.10 Access Need. The authorization screen should combine those Access Needs with existing § 5.1 Access Authorization if one exists. It should also assist the user in composing new Access Authorization, taking into account all their:
-
Data Registries with Data Registrations and Data Instances
-
§ 6.6 Access Grant with § 6.7 Data Grant others issued to them (available via all the § 6.2.1 Reciprocal Registration)
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Alice finds an Application called Projectron that she’d like to use to manage her Projects and Tasks. |
| 2 | Alice authenticates to Projectron with her WebID. |
| 3 | Projectron dereferences her WebID and retrieves Authorization Agent from her WebID Profile Document. |
| 4 | Projectron asks Alice’s Authorization Agent whether Alice already has an Application Registration for Projectron. |
| 5 | Alice’s Authorization Agent checks the Agent Registry in Alice’s Pod for a Projectron Application Registration. |
| 6 | No Application Registration for Projectron is found. Projectron now knows that Alice hasn’t given it permission to access her data, so it must ask. |
| 7 | Projectron redirects Alice to her Authorization Agent, supplying its identifier for context. |
| 8 | Alice’s Authorization Agent dereferences the supplied Projectron identifier, retrieving Projectron’s
Application profile graph and corresponding Access Need Groups from the WebID Profile Document,
as well as hasAuthorizationCallbackEndpoint.
|
| 9 | Alice’s Authorization Agent presents the Access Need Groups from Projectron’s Application profile graph, so that Alice understands what kind of data is being requested, and why. |
| 10 | Alice’s chooses the scope of access that Projectron will receive, to the data to which it has asked for access via the presented Access Needs. |
| 11-13 | Alice’s Authorization Agent records her decision as an Access Authorization in Alice’s Authorization Registry. An Application Registration is created for Projectron in Alice’s Agent Registry. An Access Grant and corresponding Data Grants are generated from the Access Authorization and stored in the Projectron Application Registration. |
| 14 | Alice’s Authorization Agent redirects her back to Projectron, now that the appropriate access has been granted. |
| 15 | Projectron again asks Alice’s Authorization Agent for a Projectron Application Registration. |
| 16 | Alice’s Authorization Agent finds the newly created Projectron Application Registration in the Agent Registry in Alice’s Pod. |
| 17 | Alice’s Authorization Agent provides the URI of the Application Registration to Projectron. |
| 18 | Projectron learns what access it received through the Access Grant in Alice’s Projectron Application Registration. |
| 19 | Projectron may now function as intended, within the scope of authorization it was given by Alice. |
8. Sharing resources indicated by the application
When the application has already been registered, and the user wants to initiate a sharing-specific § 4.2 Data Instance, an authorization flow with resource indication is available.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Alice’s is authenticated with Projectron. |
| 2 | Alice has already authorized Projectron. |
| 3 | Projectron has read its Access Grant and displayed projects. |
| 4 | Alice initiates sharing of a specific project. |
| 5 | Projectron redirects Alice to her Authorization Agent, indicating the selected project. |
| 6-8 | Alice’s Authorization Agent fetches the indicated project and checks who already has access to it. It also fetches list of all registered social agents to present it to Alice. |
| 9 | Alice chooses all the social agents with which she wants to share the selected project, as well as modes of access for all selected agents. If the shape tree has references (e.g., tasks) she can also select modes of access for each inherited shape tree. |
| 10-11 | Alice’s Authorization Agent records new access authorizations for all the selected agents and regenerates access grants provided in their agent registrations. |
| 12 | Alice’s Authorization Agent dereferences the supplied Projectron WebID, retrieving Projection’s
Application profile graph from the WebID Profile Document,
to discover the hasAuthorizationCallbackEndpoint.
|
| 13 | Alice’s Authorization Agent redirects her back to Projectron, now that the project has been shared. |
| 14 | Alice continues using Projectron. |
9. Generating Access Grant from Access Authorization
Based on an § 5.1 Access Authorization, authorization agent can generate an § 6.6 Access Grant.
For § 5.2 Data Authorization using AllFromRegistry, SelectedFromRegistry scope,
a single § 6.7 Data Grant gets generated. Similar for data authorization using Inherited scope and
inheriting from data authorization with one of those two scopes. Here a data authorization gets directly
translated into a data grant, only changing type and all authorization specific properties to grant specific properties.
For data authorization using All or AllFromAgent, zero or more data grant gets generated.
This number depends on a number of Data Registries owned by the social agent giving the authorization,
as well as number of data grants given to them by other social agents. Data authorization with Inherited scope
will also have zero or more data grants if it is inheriting from data authorization using one of those two scopes.
Example of an implementation can be found in [SAI-JS] and [SAI-JAVA]